Phytochemical screening, antioxidant and antidiabetic activities of Maerua crassifolia (Forsk) leaves, a medicinal plant used in the treatment of diabetes in Niger
Keywords:
Maerua crassifolia, Medicinal plants, Diabetes, Antioxidant, AntidiabeticAbstract
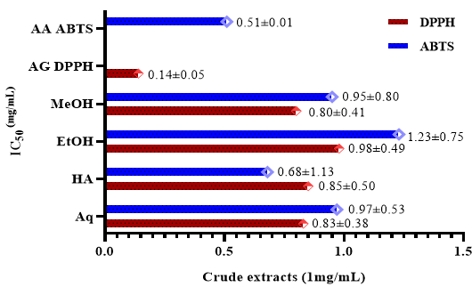
Diabetes is a pathology frequently encountered throughout the world. This disease is currently a public health problem in Africa. Medicinal plants are a source of molecules that can be used as antidiabetic agents. The present study aimed to study the phytochemistry and evaluation of antioxidant and inhibitory activities of α-amylase and α-glucosidase in vitro from crude extracts of aqueous decocted and hydroacetonic, ethanolic and methanolic macerated leaves of Maerua crassifolia. Phytochemical screening was carried out using colorimetric standards methods. The phenolics content was determined used spectrophotometric methods. The antioxidant and antidiabetic activities were evaluated. The screening revealed the presence of several secondary metabolites, such as alkaloids, tannins, flavonoids, coumarins, saponins, sterols and triterpenes. The antioxidant activity results show that the hydroacetonic extract is most active by the ABTS (2,2'-azinobis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid)) method with an IC50 (inhibitory concentration 50) equal to 0.68±1.13 mg/mL and 0.80±0.41 mg/mL with the methanolic extract by the DPPH method (2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl). The evaluation of the enzymatic inhibitory activity of the crude extracts showed inhibition percentages ranging from 61.59% to 90.07% for α-amylase and from 61.42% to 77.66% for α-glucosidase. The presence of certain secondary metabolites (flavonoids, saponosides and tannins) could justify the traditional use of Maerua crassifolia in diabetes management in Niger.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
